原发性肾病综合征是儿童时期的常见病,虽然大部分患儿经肾上腺糖皮质激素治疗后的效果较好,但是仍有相当部分患儿对激素治疗抵抗或频繁复发。故而,临床上一直在寻求既能提高激素疗效,减轻激素副作用,又能减少感染,减少病情反复的新药物和方法。近年来,中医药在儿童肾病综合征治疗中取得了一定的进展[1],但其机制仍然不清楚。除汤剂外,许多中成药免疫调节剂应用于儿科临床,已取得了一定的疗效,但是对其作用机制仍然不明,槐杞黄颗粒剂就是其中之一。
本研究以微小病变性肾病综合征大鼠模型为研究对象,从蛋白和基因水平观察槐杞黄颗粒对大鼠肾组织中nephrin和podocin表达的影响,探讨该药物对阿霉素肾病大鼠肾小球滤过屏障的影响及其作用机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验材料
20只雄性SD大鼠,体质量110~130 g,购自并饲养于复旦大学实验动物科学部,环境为清洁级,温度(20±2)℃,自由摄取饲料和水。动物使用符合上海市医学实验动物管理委员会管理条例,许可证号为SCXK(沪)2003-0002。阿霉素液射液,10 mg/支,批号为8NB002-A,购自意大利Pharmacia & Upjohn公司;强的松片,5 mg/片,批准文号为国药准字H31020675,购自上海医药有限公司信谊制药总厂;槐杞黄颗粒,10 g/包,由槐耳、枸杞子及黄精组成,每包含生药6.5 g,批号为HK12,购自启东盖天力药业有限公司;实时聚合酶链反应(polymerase chain reaction,PCR)Master Mix,批号为75660M3,购自日本TOYOBO公司;兔抗大鼠podocin抗体(批号为H2608),兔抗大鼠nephrin抗体(批号为I1208),购自美国Santa Cruz公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1动物模型制备 利用随机数字表将大鼠随机分为正常对照组、模型组、激素组、槐杞黄组和槐杞黄+激素组,每组各4只大鼠,除正常对照组外,各组大鼠经尾静脉一次性注射盐酸阿霉素7.5 mg/kg,正常对照组经尾静脉一次性注射等量生理盐水。
1.2.2 药物干预方案及动物处理 从造模后第1天起连续灌胃28 d。(1)正常对照组:经胃灌服等量蒸馏水;(2)模型组:无任何干预,正常喂养;(3)激素组:经胃灌服强的松5 mg/(kg·d);(4)槐杞黄组:经胃灌服槐杞黄颗粒剂3.3 g/(kg·d);(5)槐杞黄+激素组:同时灌服槐杞黄颗粒和强的松,剂量如上。分别在阿霉素注射后当天和第7、14、21、28天收集24 h尿液;第29天处理大鼠,处死前经腹主动脉采血3 mL;取左肾皮质1 mm×1 mm×1 mm大小数块,一部分以10%中性甲醛固定用于光学显微镜检测,另一部分以3%戊二醛固定用于电子显微镜检测;取右肾分离皮质髓质后,用消毒锡箔纸包好速冻于液氮中,后转至–70 ℃保存,用于实时荧光定量PCR及Western blot的检测。
1.3 指标检测
1.3.1 尿蛋白定量 将24 h尿液离心,取上清液与磺基水杨酸-硫酸钠试剂作用产生沉淀,所形成之浊度用比色法比浊,与同样处理的标准液比较,测得其蛋白含量。
1.3.2 光学显微镜检查 大鼠肾脏常规石蜡包埋后,平行于肾脏短轴经肾门横断修块,4 μm切片。选取含有整个肾脏断面的切片,常规苏木精和伊红染色,光学显微镜下观察肾组织病理形态改变。
1.3.3 电子显微镜检查 肾皮质用含3%戊二醛、0.22 mmol/L蔗糖的磷酸盐缓冲液(pH 7.2)固定,1%锇酸后固定,逐级乙醇脱水,环氧树脂包埋,应用日立H-600型透射电子显微镜进行肾脏超微病理学检查。
1.3.4 实时荧光定量PCR检测 取肾皮质,TRIzol法抽提总RNA,以随机六核苷酸寡聚合物为引物,采用Promega公司的M-MLV逆转录酶将其逆转录为cDNA。实时PCR用SybrGreen法,引物采用Primer Premier 5.0辅助设计,由上海生工生物工程有限公司合成。检测基因的上下游引物序列见表1。实时荧光定量PCR反应体系:上下游引物各0.5 μL,样本cDNA 0.25 μL,SYBR Mix液12.5 μL,用灭菌注射用水补足25 μL。反应条件:95 ℃预变性20 min,95 ℃变性30 s,退火30 s,72 ℃延伸40 s,40个循环。所用实时PCR扩增仪为MX3000P型(美国Stratagene公司)。mRNA表达量采用管家基因β-actin校正。
1.3.5 蛋白质印迹法检测 冰上研磨肾皮质,并加入细胞裂解液和蛋白酶抑制剂,取上清,检测蛋白浓度。加入5×十二烷基硫酸钠聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, SDS-PAGE)蛋白上样缓冲液,100 ℃加热10 min变性,10% SDS-PAGE电泳,每孔上样总蛋白150 μg。电泳后用湿法将蛋白转移到硝酸纤维素膜上,室温下10%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h,分别加入podocin抗体(1︰250稀释)、nephrin抗体(1︰100),室温孵育3 h后,收入4 ℃冰箱内过夜。TBST洗膜后,加入辣根过氧化物酶标记的羊抗兔IgG和甘油醛-3-磷酸脱氢酶(glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, GAPDH)(均1︰5 000稀释),室温孵育1 h,洗膜后,加入电化学发光剂(美国Thermo公司),采用LAS-4000 Mini型发光成像分析仪(日本富士公司)对膜进行曝光时间叠加拍照,后应用仪器自带软件Multi Gauge Ver3.X 对检测蛋白和GAPDH蛋白条带的光密度进行分析。
1.4 统计学方法
实时PCR结果取对数后进行统计,蛋白质印迹目的蛋白光密度值与对应GAPDH蛋白光密度值的比值除以正常对照组比值后进行统计分析。应用SPSS 15.0统计软件进行分析,数据以x±s表示;对于24 h尿蛋白量的比较,采用一般线性模型的Repeated Measure过程实现重复测量资料的方差分析,并用Multivariate过程实现组间的两两比较;对于实时PCR和Western blot结果,采用析因设计的方差分析进行比较;同时采用Pearson法做线性相关性分析。P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 各组大鼠24 h尿蛋白定量
各组大鼠造模前尿蛋白均在同一基线上。阿霉素注射后第7天,模型组及药物干预组大鼠24 h尿蛋白量开始增加,但与正常对照组比较无统计学意义。在第14天时,模型组24 h蛋白量较正常对照组增加(P=0.005),槐杞黄组同正常对照组比较差异亦有统计学意义(P=0.021)。在第21天时,与正常对照组相比,模型组、激素组、槐杞黄组24 h尿蛋白量显著增加(P=0.015,P=0.045,P=0.028);而槐杞黄+激素组尿蛋白含量与正常对照组比较差异无统计学意义(P=0.185)。在第28天时,与正常对照组相比,模型组和槐杞黄组24 h尿蛋白量显著增加(P=0.012,P=0.032);而激素组和槐杞黄+激素组与正常对照组间比较差异无统计学意义。此外,在各时间点,3个药物干预组与模型组相比,差异无统计学意义。见表2。
Table 2 Content of 24-hour urinary protein of rats in different groups
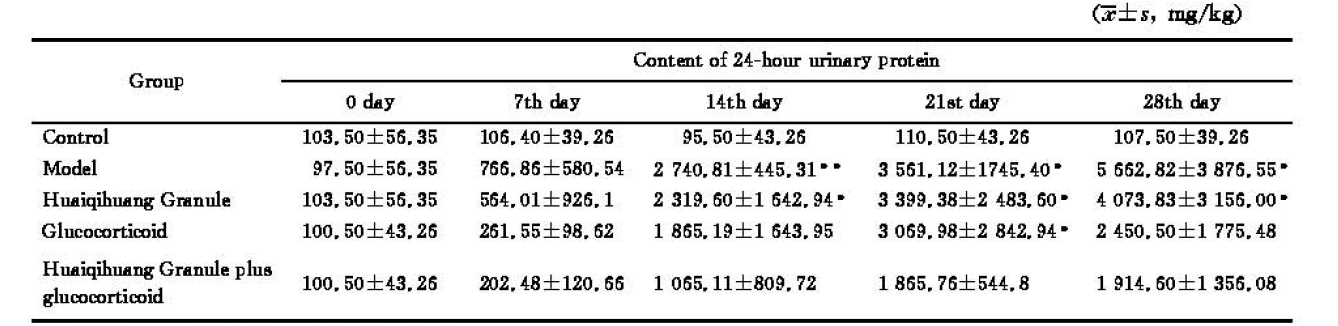 |
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, vs control group.
2.2 各组大鼠肾组织病理形态学改变
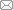
正常对照组大鼠肾组织无明显病变。模型组大鼠部分肾小球体积稍增大,系膜细胞及基质局灶节段性轻度增多,但未见坏死、新月体及硬化;肾小管上皮细胞可见部分灶性颗粒样、空泡样变性,小管未见明显萎缩,偶见小管有蛋白管型;肾间质有灶性炎症细胞浸润,伴少量纤维组织增生;部分小动脉内膜增厚。激素组、槐杞黄组及槐杞黄+激素组肾组织病理改变较模型组好转,肾间质炎症细胞浸润减少。见图1。
图1
图1
光学显微镜下各组肾病大鼠肾组织(苏木精和伊红染色,×400)
Figure 1
Pathological changes of renal tissues of rats under the light microscope (Hematoxylin and eosin staining, ×400)
A: Control group; B: Model group; C: Huaiqihuang Granule group; D: Glucocorticoid group; E: Huaiqihuang Granule plus glucocorticoid group.
2.3 各组大鼠透射电子显微镜观察的肾脏超微病理改变
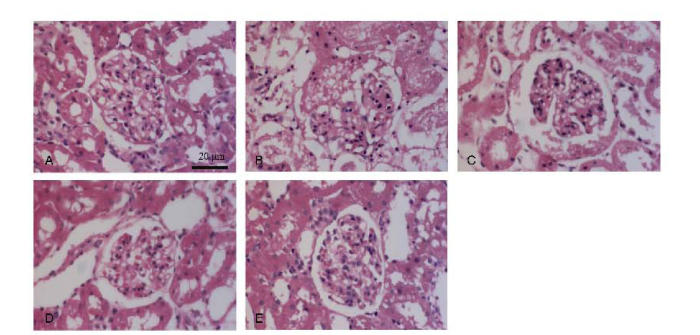
正常对照组肾小球基底膜光滑均匀,未见增厚,足突清晰完整、未见融合。模型组肾小球基底膜偶见增厚,但足突大部分融合、消失,或出现部分微绒毛,与正常对照组有明显差异,达到临床上微小病变型肾病病理诊断标准,证明模型成功建立。槐杞黄组大鼠肾小球基底膜基本光滑均匀,足突融合明显减轻,有少量新生绒毛长出;激素组及槐杞黄+激素组大鼠,足突清晰,甚至接近正常对照组,好转程度尤以槐杞黄+激素组最为明显。见图2。
图2
图2
电子显微镜下各组大鼠肾病足突形态变化(×7 000)
Figure 2
Ultra-structural changes of foot processes of renal tissues of rats under the electron microscope (×7 000)
A: Control group; B: Model group; C: Huaiqihuang Granule group; D: Glucocorticoid group; E: Huaiqihuang Granule plus glucocorticoid group.
2.4 各组大鼠肾组织nephrin及podocin mRNA的表达
在建模后第29天,模型组大鼠肾组织nephrin mRNA表达明显低于正常对照组(P=0.014),激素及槐杞黄的应用和槐杞黄+激素的交互作用对提高nephrin mRNA的表达均有统计学意义,其中槐杞黄+激素的交互作用具有统计学意义(P=0.015,P=0.043,P=0.003)。模型组大鼠肾组织podocin mRNA表达明显低于正常对照组(P=0.007),激素的应用对上调podocin mRNA的表达具有统计学意义(P=0.031),其中,槐杞黄的应用和槐杞黄+激素的交互作用在此方面的统计学意义更为显著(P=0.001,P=0.006)。见表3。
Table 3 Expressions of nephrin and podocin mRNAs in renal tissue of rats in different groups
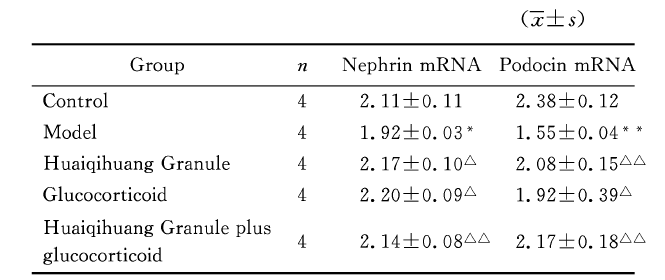 |
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, vs control group; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01, vs model group.
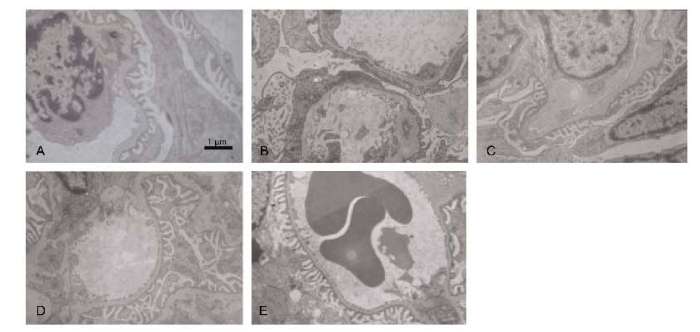
2.5 各组大鼠肾组织nephrin及podocin蛋白的表达
Table 4 Expressions of nephrin and podocin proteins in renal tissue of rats in different groups
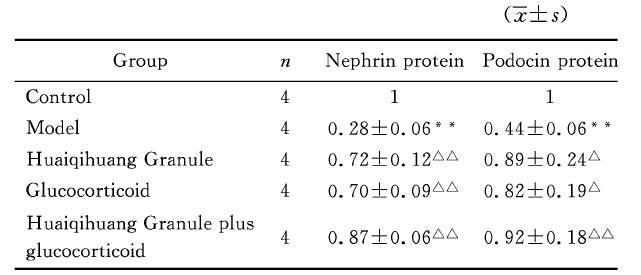 |
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, vs control group; △P<0.05, △△P<0.01, vs model group.
图3
图3
Western blot法检测nephrin及podocin蛋白的表达
Figure 3
Expressions of nephrin and podocin proteins observed by Western blot method
A: Control group; B: Model group; C: Huaiqihuang Granule group; D: Glucocorticoid group; E: Huaiqihuang Granule plus glucocorticoid group.
2.6 肾组织nephrin和podocin表达与24 h尿蛋白排泄量的相关性分析
在建模后第29天,大鼠肾组织中nephrin mRNA、nephrin和podocin蛋白的表达与24 h尿蛋白排泄量呈负相关(r=-0.587, P=0.011; r=-0.611, P=0.007; r=-0.547, P=0.019);而podocin mRNA的表达与24 h尿蛋白排泄量无关(r=–0.282, P=0.257)。
3 讨论
中医学认为,原发性肾病综合征多属“水肿”、“尿浊”范畴,其病理本质为本虚标实,以脾肾两虚为本,以血瘀、湿浊为辅。该病主要表现之一为大量蛋白尿的产生,其中脾肾两虚是蛋白尿产生的直接机制,此外,肺虚、湿热亦可引起蛋白尿。
目前研究认为,蛋白尿的产生与肾小球滤过屏障正常的结构遭到破坏和(或)其功能损伤有着十分密切的关系。肾小球滤过屏障由内皮细胞窗孔、肾小球基底膜和脏层细胞足突之间的裂孔隔膜组成,而影响蛋白滤过的主要屏障是足突裂孔隔膜,由“拉链样结构”组成,其中央为线状结构,两侧为横桥结构,横桥间为4 nm×14 nm的孔隙。该孔稍小于白蛋白分子的大小,起分子屏障作用,由podocin、nephrin、CD2AP、ACTN4、FAT、TRPC6和PLCE1等多种蛋白质分子组成[6]。Nephrin是一种跨膜蛋白,胞内部分含有8个酪氨酸残基,当nephrin与其配基结合时,可能导致胞内酪氨酸残基磷酸化,从而将信号传入细胞内以发挥其生物效应。Nephrin特异性表达在裂孔膜上,是裂孔膜蛋白复合体的主要成分[7]。研究发现,在阿霉素肾病大鼠中,nephrin在蛋白尿的产生和小球基膜延展方面具有重要作用;nephrin是该疾病中最敏感的分子[8]。Podocin也是一种跨膜蛋白,属stomatin家族。原位杂交显示编码podocin的基因NPHS2几乎全部表达在肾小球足细胞,而不在其他组织部位表达;podocin通过其C末端与nephrin及CD2AP的胞内段相互作用,可促进或放大nephrin诱导的信号传导[9]。
本实验采用一次性尾静脉注射阿霉素7.5 mg/kg制备肾病微小病变型模型[10],并且每隔1周测定各组蛋白尿情况。我们发现,模型组在第2周后尿蛋白量明显增高(P=0.005),第4周时达高峰(P=0.012);同时,电子显微镜观察模型组肾小球足细胞足突融合明显,由此可以判断造模较为理想。此外,药物干预28 d后,蛋白尿排泄量均不同程度下降,尤以槐杞黄+激素组干预效果最为明显;但是在槐杞黄组中,其尿蛋白量控制不佳。肾组织电子显微镜观察显示,3个治疗组大鼠在阿霉素注射后28 d肾小球足细胞足突部分融合较模型组减轻,尤以槐杞黄+激素组最为明显,足突融合基本消失。以上实验结果表明,槐杞黄颗粒联合氢化可的松对阿霉素肾病大鼠模型有保护作用。
本研究发现,与正常对照组相比,模型组中的podocin、nephrin mRNA及蛋白水平的表达明显降低(均P<0.01),提示podocin、nephrin在肾病综合征的发生和蛋白尿的产生过程中起到了一定的作用。此外,与模型组相比,各治疗组podocin、nephrin mRNA及蛋白水平的表达都不同程度的增加,尤以槐杞黄+激素组增加明显(P<0.01)。以上结果提示,槐杞黄颗粒可能通过稳定裂孔隔膜上的podocin及nephrin蛋白,维持肾小球滤过屏障,以降低尿蛋白漏出,并且槐杞黄颗粒与激素合用干预效果更好,这也为临床上益气养阴方辅助激素治疗肾病综合征提供了理论依据。
本实验亦发现,大鼠肾组织中nephrin和podocin的表达与24 h尿蛋白排泄量呈负相关,不仅提示了蛋白尿的发生与nephrin和podocin蛋白的相关性,亦说明槐杞黄颗粒通过上调nephrin和podocin蛋白的表达,维持了滤过屏障上裂孔隔膜的完整性,减少了蛋白尿的产生,从而保护肾脏。
本实验从裂孔隔膜分子nephrin和podocin蛋白入手,初步探讨了槐杞黄颗粒对减少阿霉素肾病大鼠蛋白尿产生和保护肾小球滤过屏障的机制。进一步的研究方向,可以选择不同的干预时间点或选择肾小球滤过屏障上的其他分子,以求更深入地了解槐杞黄的作用机制。
4 利益冲突
本文作者声明不存在任何与本稿件相关的利益冲突。
Reference
Systematic analysis of therapy of the primary nephrotic syndrome with the traditional Chinese and Western medicine combination
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2007.04.008
URL
Magsci
[Cited within: 1]

[目的]应用Meta-分析评价中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征是否有助于提高疗效;中西医结合治疗对难治性肾病综合征是否亦能提高疗效.[方法]以中西医结合、原发性肾病综合征为主题词,采用电子和手工检索中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM disc)、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI,1994~2006.12)、维普中文科技期刊数据库(1989~)、中国循证医学/Cochrane 中心数据库(CEBM/CCD)、Cochrane图书馆等数据库,搜集关于中西结合治疗原发性肾病综合征的随机对照试验(RCTs);采用Cochrane协作网专用软件RevMan4.2进行统计分析.[结果]检索符合RCTs纳入标准的治疗原发性肾病综合征的随机对照试验16篇,共584例病人;治疗小儿原发性肾病综合征的随机对照实验4篇,共101例病人;治疗难治性肾病综合征的随机对照实验4篇,共181例病人,Meta分析显示中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征可以提高完全缓解率,降低复发率,对难治性肾病及小儿原发性肾病综合征亦有效.[结论]中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征可以提高疗效,减少复发;中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征确切疗效尚有待于设计严格的多中心、大样本随机对照实验进一步证实.
中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征的系统评价
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-7171.2007.04.008
URL
Magsci
[Cited within: 1]

[目的]应用Meta-分析评价中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征是否有助于提高疗效;中西医结合治疗对难治性肾病综合征是否亦能提高疗效.[方法]以中西医结合、原发性肾病综合征为主题词,采用电子和手工检索中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM disc)、中国期刊全文数据库(CNKI,1994~2006.12)、维普中文科技期刊数据库(1989~)、中国循证医学/Cochrane 中心数据库(CEBM/CCD)、Cochrane图书馆等数据库,搜集关于中西结合治疗原发性肾病综合征的随机对照试验(RCTs);采用Cochrane协作网专用软件RevMan4.2进行统计分析.[结果]检索符合RCTs纳入标准的治疗原发性肾病综合征的随机对照试验16篇,共584例病人;治疗小儿原发性肾病综合征的随机对照实验4篇,共101例病人;治疗难治性肾病综合征的随机对照实验4篇,共181例病人,Meta分析显示中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征可以提高完全缓解率,降低复发率,对难治性肾病及小儿原发性肾病综合征亦有效.[结论]中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征可以提高疗效,减少复发;中西医结合治疗原发性肾病综合征确切疗效尚有待于设计严格的多中心、大样本随机对照实验进一步证实.
The effect of Trametes robiniophila Murr.(TRM) substantial composition on immune function of mice
[J].Through solid fermentation in nutrient substratum, Trametes robiniophila Murr. (TRM), used as a famous medicinal fungi in ancient china, produced fungal substance from which clear paste and further isolated proteoglycan had been extracted. Both clear paste and proteo'glycan had tumor-inhibition effect on experimental animals and prolonged the life of infected animals And the tumor inhibition rate ia about 50%. Patients with middle or later period primary hepatoma treated with the paste, had got a total efficient rate of about 75%. Both the TRM clear paste and the proteoglycan promoted various immune functions. They are good biological response modifier and may be used to treat other adaptive diseases.
槐耳菌质成分对小鼠免疫功能的影响
[J].Through solid fermentation in nutrient substratum, Trametes robiniophila Murr. (TRM), used as a famous medicinal fungi in ancient china, produced fungal substance from which clear paste and further isolated proteoglycan had been extracted. Both clear paste and proteo'glycan had tumor-inhibition effect on experimental animals and prolonged the life of infected animals And the tumor inhibition rate ia about 50%. Patients with middle or later period primary hepatoma treated with the paste, had got a total efficient rate of about 75%. Both the TRM clear paste and the proteoglycan promoted various immune functions. They are good biological response modifier and may be used to treat other adaptive diseases.
Clinical research on effects of Huai’er granule on quality of life and immune function of patients receiving chemotherapy
[J].
槐耳颗粒对化疗患者生活质量及免疫功能影响的临床研究
[J].
The impact of Huai’er granule to Th1/Th2 shift on patients with primary hepatic cancer after surgical resection
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-9523.2008.09.004
URL
[Cited within: 1]

目的研究槐耳颗粒对原发性肝癌(PHC)手术切除后病人Th1/Th2漂移的影响。方法以IFN-1和IL-2代表Th1类细胞因子,IL4和IL-10代表Th2类细胞因子,以反转录聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)检测18例原发性肝癌患者术前和术后40d即服用槐耳颗粒1个月后外周血单个核细胞(PBMC)Th1/Th2类细胞因子mRNA的表达,以20例原发性肝癌单纯手术切除患者作为对照。结果槐耳颗粒组与单纯手术切除组比较术前Th1型细胞因子表达无显著差异,术后40dTh1型细胞因子表达明显增高,有差异有统计学意义(P=0.025)。结论服用槐耳颗粒促使PHC手术切除后患者转向Th1状态。
槐耳颗粒对原发性肝癌术后Th1/Th2漂移的影响
[J].
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-9523.2008.09.004
URL
[Cited within: 1]

目的研究槐耳颗粒对原发性肝癌(PHC)手术切除后病人Th1/Th2漂移的影响。方法以IFN-1和IL-2代表Th1类细胞因子,IL4和IL-10代表Th2类细胞因子,以反转录聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)检测18例原发性肝癌患者术前和术后40d即服用槐耳颗粒1个月后外周血单个核细胞(PBMC)Th1/Th2类细胞因子mRNA的表达,以20例原发性肝癌单纯手术切除患者作为对照。结果槐耳颗粒组与单纯手术切除组比较术前Th1型细胞因子表达无显著差异,术后40dTh1型细胞因子表达明显增高,有差异有统计学意义(P=0.025)。结论服用槐耳颗粒促使PHC手术切除后患者转向Th1状态。
Molecular genetic analysis of podocyte genes in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis — a review
[J].
DOI:10.1007/s00431-009-1017-x
URL
PMID:19562370
[Cited within: 1]

This review deals with podocyte proteins that play a significant role in the structure and function of the glomerular filter. Genetic linkage studies has identified several genes involved in the development of nephrotic syndrome and contributed to the understanding of the pathophysiology of glomerular proteinuria and/or focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Here, we describe already well-characterized genetic diseases due to mutations in nephrin, podocin, CD2AP , alpha-actinin-4, WT1, and laminin 2 chain, as well as more recently identified genetic abnormalities in TRPC6, phospholipase C epsilon, and the proteins encoded by the mitochondrial genome. In addition, the role of the proteins which have shown to be important for the structure and functions by gene knockout studies in mice, are also discussed. Furthermore, some rare syndromes with glomerular involvement, in which molecular defects have been recently identified, are briefly described. In summary, this review updates the current knowledge of genetic causes of congenital and childhood nephrotic syndrome and provides new insights into mechanisms of glomerular dysfunction.
Nephrin is specifically located at the slit diaphragm of glomerular podocytes
[J].DOI:10.1073/pnas.96.14.7962 URL [Cited within: 1]
Dissociation of NEPH1 from nephrin is involved in development of a rat model of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis
[J].DOI:10.1152/ajprenal.00075.2008 URL [Cited within: 1]
Role of nephrin in renal disease including diabetic nephropathy
[J].
DOI:10.1053/snep.2002.34724
URL
[Cited within: 1]

Nephrin, a newly described protein, has been localized to the slit membrane between adjacent podocytes of the glomerulus. Its discovery followed the demonstration of the gene NPHS1 and its mutation, resulting in the absence of the protein product, nephrin, in the congenital nephrotic syndrome of the Finnish type. The link between permutations in nephrin expression and proteinuria has been shown in animal models by using neutralizing antibodies or studying mice with inactivation of the nephrin gene. Moreover, the expression of nephrin has been shown to be reduced in various animal models of proteinuric renal disease. The relationship between changes in nephrin expression and proteinuric renal disease in humans is not fully elucidated, with a reduction in expression of this protein reported in a range of renal diseases. Diabetic nephropathy, one of the major causes of end-stage renal disease, is associated with substantial proteinuria and in experimental models with a reduction in slit pore density. In experimental models of diabetes, nephrin expression has been described as being transiently increased in the first 8 weeks of diabetes, followed in longer-term studies with reduced nephrin expression in association with increasing proteinuria. An angiotensin II-receptor blocker has been shown to prevent depletion in glomerular nephrin expression in the diabetic kidney. Human studies in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes suggest down-regulation of nephrin expression in the diabetic kidney and it has been postulated that these changes may play a role in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy, specifically the development of proteinuria in this condition. Although there are other proteins involved in the structure of the epithelial podocyte and specifically the slit pore, nephrin seems to play a pivotal role in preventing passage of protein through the glomerular barrier. Furthermore, it is suggested that the antiproteinuric effects of inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system may partly relate to the effects of these agents on nephrin expression. Copyright 2002, Elsevier Science (USA). All rights reserved.
Adriamycin-induced nephropathy as a model of chronic progressive glomerular disease
[J].
DOI:10.1038/ki.1986.28
URL
PMID:3486312
[Cited within: 1]

Serial changes in urine protein, blood chemistry, and histology of the kidney were investigated in rats for 28 weeks after injections of adriamycin (ADR). Massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and hyperlipidemia were observed at week 4 and throughout the experiment. Both BUN and serum creatinine began to increase at week 16 and reached the uremic level at week 28. Light microscopic study of the kidney demonstrated a normal appearance at week 4, vacuole formation in glomerular tuft at weeks 8 and 12, focal and segmental glomerular sclerosis at weeks 16 and 20, and extensive glomerular sclerosis with tubulointerstitial degenerations at weeks 24 and 28. Immunohistologically, IgM with a small amount of IgG and C3 appeared in the sclerosing glomeruli from week 16. Aggregated human IgG, injected intravenously at week 24, had accumulated mainly in the glomeruli. Electron microscopy revealed degenerative changes of glomerular epithelial cells with small vacuoles in the cytoplasm at week 4. Size of vacuoles increased at the later stage. In conclusion, ADR produced chronic, progressive glomerular changes in rats, which led to terminal renal failure. The segmental glomerular sclerosis and IgM-dominant glomerular deposition in these animals are similar to pathological characteristics of focal and segmental glomerular sclerosis seen clinically.