Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine ›› 2009, Vol. 7 ›› Issue (5): 418-421.doi: 10.3736/jcim20090504
• Original Clinical Research • Previous Articles Next Articles
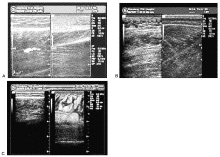
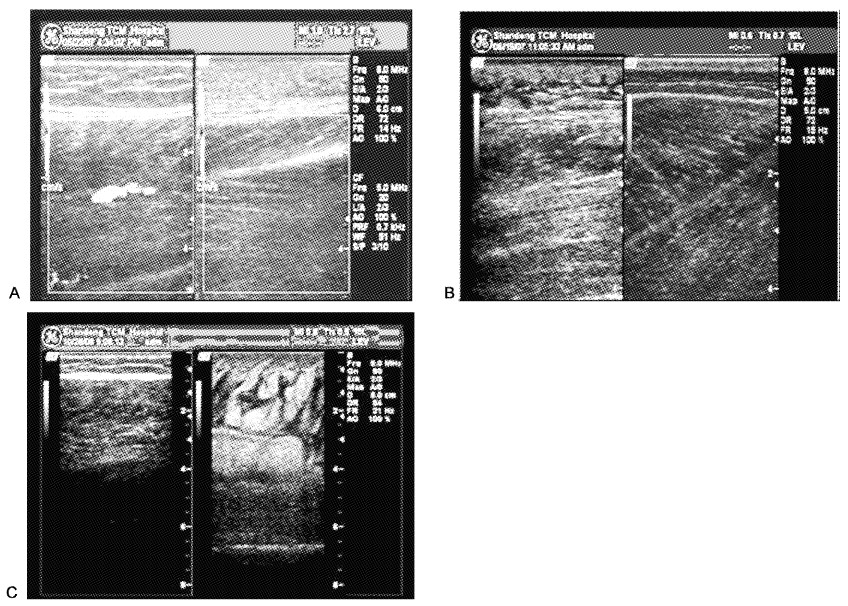
Relationship between ultrasound imaging and traditional Chinese medicine syndrome in limb lymphedema
Ming Liu , Yue Zhang, Fu-chen Song, Zhi-xing Cheng
, Yue Zhang, Fu-chen Song, Zhi-xing Cheng
- Department of Peripheral Vascular Surgery, Affiliated Hospital, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250011, Shandong Province, China
| [1] | Chen BN, Hou YF, Zhou T. Diagnosis and treatment of peripheral vascular diseases in Chinese and Western medicine[M]. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine,1999: 509-512 |
| 陈柏楠, 侯玉芬, 周涛 . 周围血管疾病中西医诊疗学[M]. 北京: 中国中医药出版社,1999: 509-512 | |
| [2] | Zhou LL, Zhang XJ . Ultrasound diagnosis of extremity lymphedema[J]. Zhongguo Chao Sheng Yi Xue Za Zhi, 2003,19(3):218-219 |
| 周黎丽, 张晓杰 . 肢体淋巴水肿的超声诊断[J]. 中国超声医学杂志, 2003,19(3):218-219 | |
| [3] | Liu XM, Zhang Y, Liu M . Diagnostic value of ultrasound in researching traditional Chinese medicine syndrome[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Ying Xiang Xue Za Zhi, 2008,6(4):293-295 |
| 刘效敏, 张玥, 刘明 . 超声在中医证型客观化研究中的应用价值[J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2008,6(4):293-295 |
| [1] | Qi-sheng Tang, Wen-jun Sun, Miao Qu, Dong-fang Guo. Analysis of syndrome discipline of generalized anxiety disorder using data mining techniques. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(9): 975-982. |
| [2] | Lu Liu, Ying Gao. Study on the correlation between traditional Chinese medicine syndrome and short-term prognosis of ischemic stroke using logistic regression model and repeated-measures analysis of variance. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(9): 983-990. |
| [3] | Yan Guan , Hui Zhang, Wei Zhang, Shi-bing Su . Analysis of differential gene expression profile in peripheral blood of patients with chronic hepatitis B and syndromes of dual deficiency of liver and kidney yin and accumulation of dampness heat. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(7): 751-756. |
| [4] | Ying-fei Bi , Jing-yuan Mao , Xian-liang Wang , Ya-zhu Hou , Yi-zhu Lu , Shan Bin Soh , Bo-li Zhang. Clinical epidemiology survey of the traditional Chinese medicine etiology and syndrome differentiation of coronary artery disease: Study protocol of a multicenter trial. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(6): 619-627. |
| [5] | Qing-bo Lang, Dong-xia Zhai , Feng Huang, Jian-guo Chen, Yong-hui Zhang, Qun Liu, Xiao-feng Zhai , Bai Li, Chang-quan Ling. Investigation on traditional Chinese medicine syndrome distribution of 4 618 hepatitis B virus infection subjects in Qidong of Jiangsu Province, China. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(5): 525-531. |
| [6] | Jia-jia Wang , Tian-fang Wang , Xiu-yan WU , Yah Zhao , Xiao-lin Xue , Qing-guo Wang. Weighting coefficients of symptoms and signs in the diagnosis of corresponding TCM syndrome elements of ulcerative colitis based on expert questionnaire investigation. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(4): 398-405. |
| [7] | Hu Xiao-Yu, Zhang Yang, Chen Guo, Zhong Sen, Fan Xin-Jian. A prospective cohort study on the influence of high doses of herbs for clearing heat and resolving stasis on survival rates in patients with hepatitis B-related acute-on-chronic liver failure. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(2): 176-185. |
| [8] | Yu Zhao, Jing-hua Peng , Xue-mei Li , Qi-lin Fu, Tuan Cui , Qi Li, Ya-jun Tang , Qin Feng , Hua Zhang , Hua Zhou , Yi-yang Hu. Diagnostic value of clinical indices in syndrome differentiation of chronic hepatitis B: an exploration based on receiver operating characteristic curves and stepwise discriminant analysis. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(12): 1382-1387. |
| [9] | Dong-tao Li, Jian Wang , Hong-yang Jiang , Feng-lei Shi , Fu-yu Li , Ji-hong Liu , Yong-mei Cheng , Nan Yan , Ai-hua Hu, Mei-zeng Zhang , Jie Li, Ling-bo Wei , Rong-qin Jiang. Quantitative evaluation of the degrees of traditional Chinese medicine qualitative syndromes of osteoporosis. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(11): 1254-1262. |
| [10] | Jing Zhang , Long Liu , Xin Yan , Xiao-qiang Yue. Study of the syndromes of traditional Chinese medicine in terms of metabonomics technology: The current situation and considerations. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(10): 1069-1076. |
| [11] | Gui-xiang Chu, Qing-guang Chen, Jia-tuo Xu , Bo Yu , Min Zhang , Long-tao Cui , Hong-jin Wu , Zhao-fu Fei. Analysis on pulse diagram characteristics of subjects with subhealth state. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(10): 1099-1105. |
| [12] | Liu Yue, Xie Ming, Zhang Ye. Dynamic changes of laboratory parameters of rats with type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance: defining their role in development of traditional Chinese medicine syndrome. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2012, 10(1): 100-108. |
| [13] | Xing-jiang Xiong, Hai-xia Li . Experience on clinical application of Chinese herbal medicine Yi Guan Jian decoction. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2011, 9(8): 920-923. |
| [14] | Ji Sun, Sheng-liang Zhu, Shu-ying Ma, Xiao-su Wang, Jing Kong. Clinical characteristics of patients with reflux esophagitis exhibiting gallbladder heat attacking the stomach or stagnant heat of the liver and stomach syndrome. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2011, 9(7): 732-736. |
| [15] | Tian-fang Wang, Xiao-lin Xue, Ya-jing Zhang, Ping Han, Zhen Li, Wen-ping Wang, Jian-min Xing, Qing-bo Wang, Yu Tang, Li Li, Jia-jia Wang, Guan-ru Li, Shao-liang Ji, Liu-xin Wu, Yan Zhao, Xiu-yan Wu, Run-shuan Zhao. Effects of Xiaopi Yishen herbal extract granules in treatment of fatigue-predominant subhealth due to liver-qi stagnation and spleen-qi deficiency: A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled and double-blind clinical trial. Journal of Chinese Integrative Medicine, 2011, 9(5): 515-524. |
|